Civil War
Discover how the American Civil War shaped the United States and changed the course of history!
What Was the American Civil War?
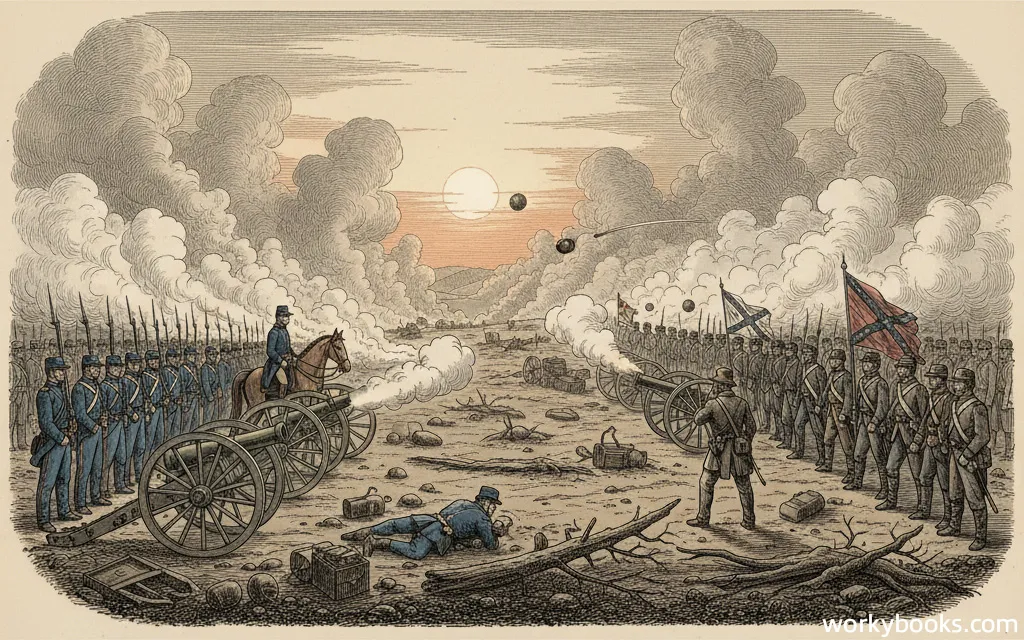

The American Civil War was a major conflict fought in the United States from 1861 to 1865. It was fought between the Northern states (called the Union) and the Southern states (called the Confederacy). The war was the deadliest in American history, with over 600,000 soldiers killed.
The Civil War began when Southern states decided to leave the United States (a process called secession) and form their own country called the Confederate States of America. The Northern states believed the country should stay united. The war ended when the Confederate armies surrendered and the Southern states rejoined the United States.
Did You Know?
The American Civil War was fought in over 10,000 locations across the United States, from Pennsylvania to New Mexico, and from Florida to Kansas.
Causes of the Civil War
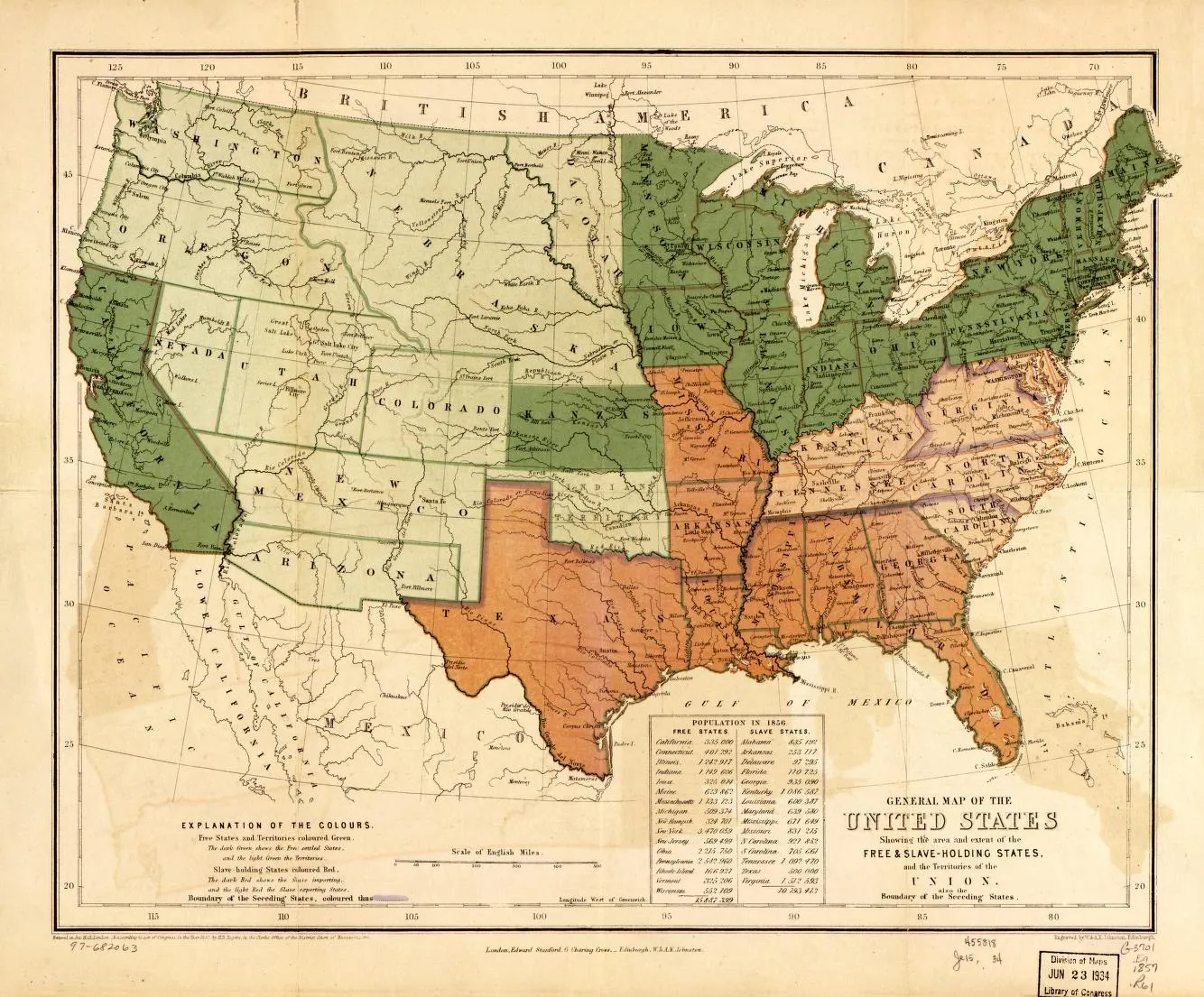
Map of the United States showing free states and slave states before the Civil War
The Civil War had several important causes, but the most significant was the issue of slavery. The Southern economy depended on enslaved African Americans to work on large farms called plantations. The Northern states had mostly ended slavery and wanted to stop it from spreading to new territories.
Other important causes included disagreements about states' rights (whether states could make their own laws independent of the federal government) and economic differences between the industrial North and agricultural South.
Slavery
The disagreement over whether slavery should be allowed to expand to new territories
States' Rights
Arguments over how much power states should have versus the federal government
Economic Differences
The industrial North versus the agricultural South created different needs and interests
Major Battles of the Civil War
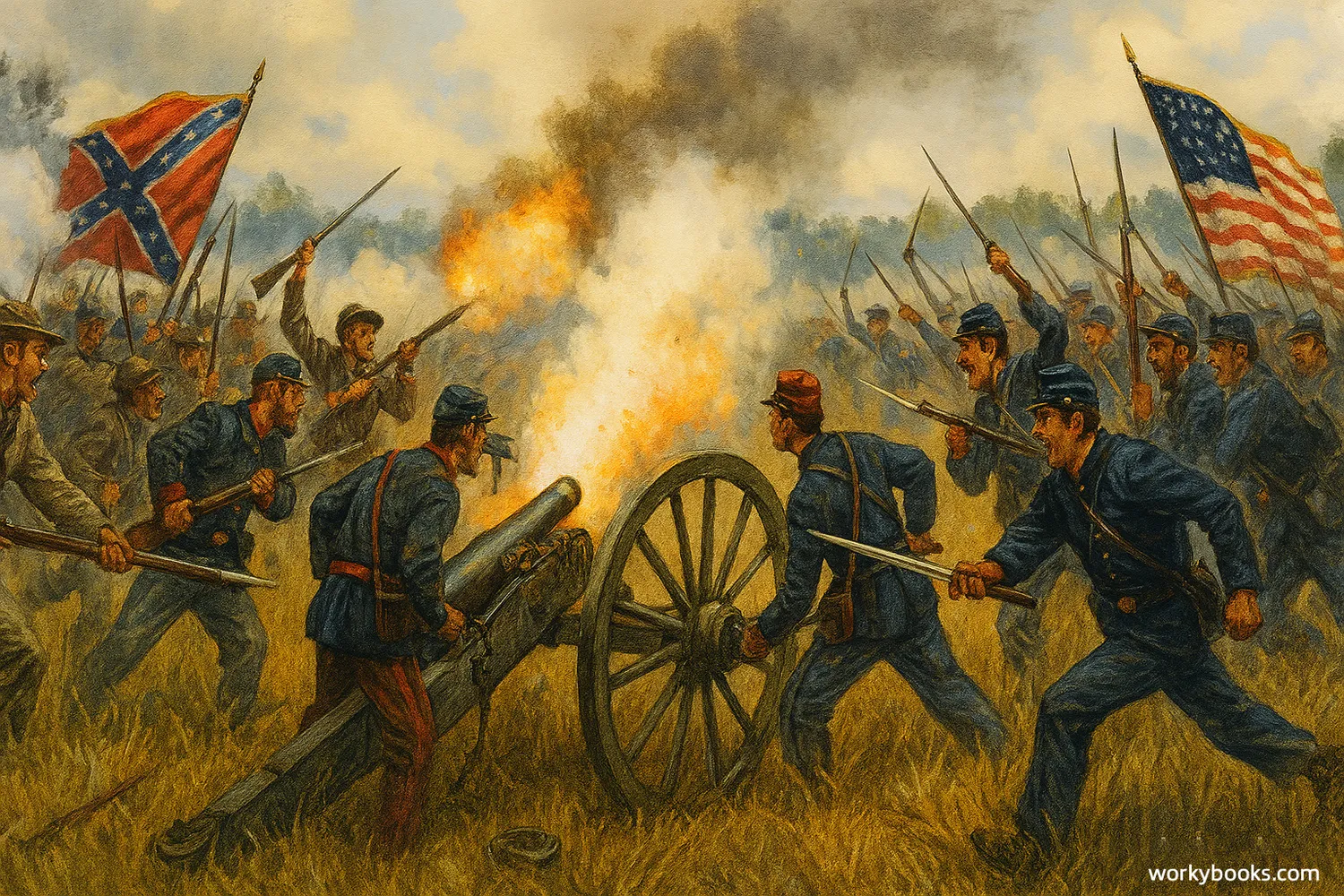

The Civil War included many important battles that determined its outcome. Some of the most significant battles were:
- Fort Sumter (1861) - The first battle of the Civil War in South Carolina
- Battle of Bull Run (1861) - The first major battle that showed the war would be long and difficult
- Battle of Antietam (1862) - The bloodiest single day in American military history
- Battle of Gettysburg (1863) - The turning point of the war where the Union stopped the Confederate invasion of the North
- Siege of Vicksburg (1863) - Gave the Union control of the Mississippi River
- Battle of Atlanta (1864) - Helped ensure President Lincoln's reelection
These battles were important because they determined which side would control key territories and resources. The Union's victories at Gettysburg and Vicksburg in 1863 were especially important turning points.
Important Leaders of the Civil War

Both the Union and Confederacy had important military and political leaders:
Union Leaders
Abraham Lincoln - President of the United States
Ulysses S. Grant - Top Union general
William T. Sherman - Union general known for his "March to the Sea"
Confederate Leaders
Jefferson Davis - President of the Confederacy
Robert E. Lee - Top Confederate general
Stonewall Jackson - Skilled Confederate general
These leaders made important decisions that affected the course of the war. President Lincoln's leadership kept the Union together, while General Lee's military skills helped the Confederacy win several early battles.
The Emancipation Proclamation
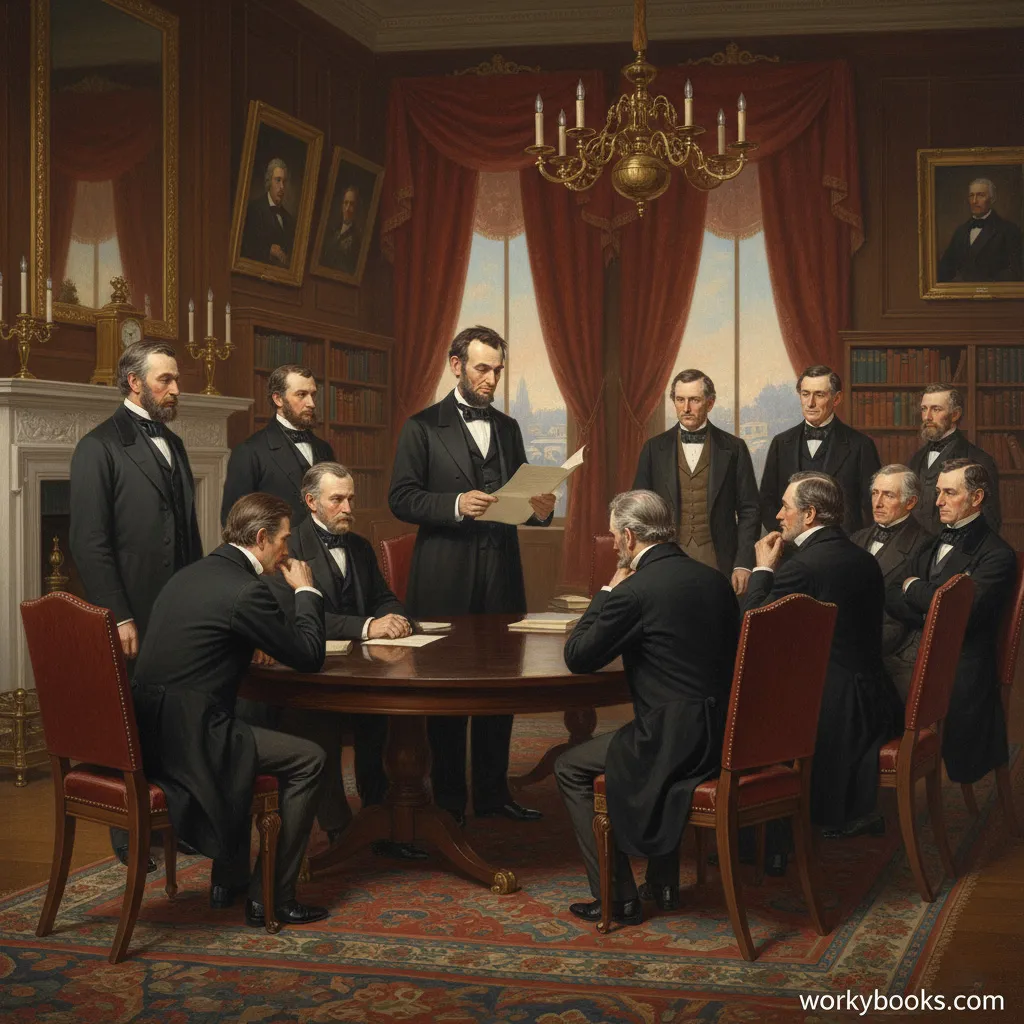

The Emancipation Proclamation was an important document issued by President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863. It declared that all enslaved people in Confederate states "shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free."
While the proclamation didn't immediately free all enslaved people (it only applied to states in rebellion), it changed the purpose of the war. The Union was now fighting not just to preserve the country, but also to end slavery.
Important Effects of the Emancipation Proclamation:
- Changed the war's purpose from preserving the Union to ending slavery
- Encouraged African Americans to join the Union Army
- Prevented European countries from supporting the Confederacy
- Paved the way for the 13th Amendment, which ended slavery everywhere in the U.S.
Civil War Timeline
The American Civil War unfolded over four years with many important events:
War Begins
Confederate forces attack Fort Sumter; first Battle of Bull Run
Major Battles
Battle of Antietam becomes bloodiest single day; Union captures New Orleans
Turning Point
Emancipation Proclamation; Union victories at Gettysburg and Vicksburg
Union Advances
Sherman's March to the Sea; Lincoln reelected
War Ends
Lee surrenders at Appomattox; Lincoln assassinated; 13th Amendment passed
This timeline shows how the war progressed from the initial Confederate successes to eventual Union victory. The year 1863 was especially important as the turning point when the Union began to gain the upper hand.
Civil War Quiz
Test your knowledge about the American Civil War! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the American Civil War:
Civil War Trivia
Discover amazing facts about the American Civil War!
Horses in the War
Over 1 million horses and mules died during the Civil War. These animals were essential for transportation, cavalry charges, and pulling artillery.
Young Soldiers
Many soldiers were very young - some as young as 12 fought in the war. The average age of a Union soldier was 25.8 years.
First Photographed War
The Civil War was the first American war to be extensively photographed. These images showed people the reality of war for the first time.
Ironclad Ships
The Civil War featured the first battle between ironclad warships - the USS Monitor and the CSS Virginia (formerly the USS Merrimack).





