Aquatic Biome - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover water ecosystems from freshwater streams to deep ocean habitats!
What are Aquatic Biomes?
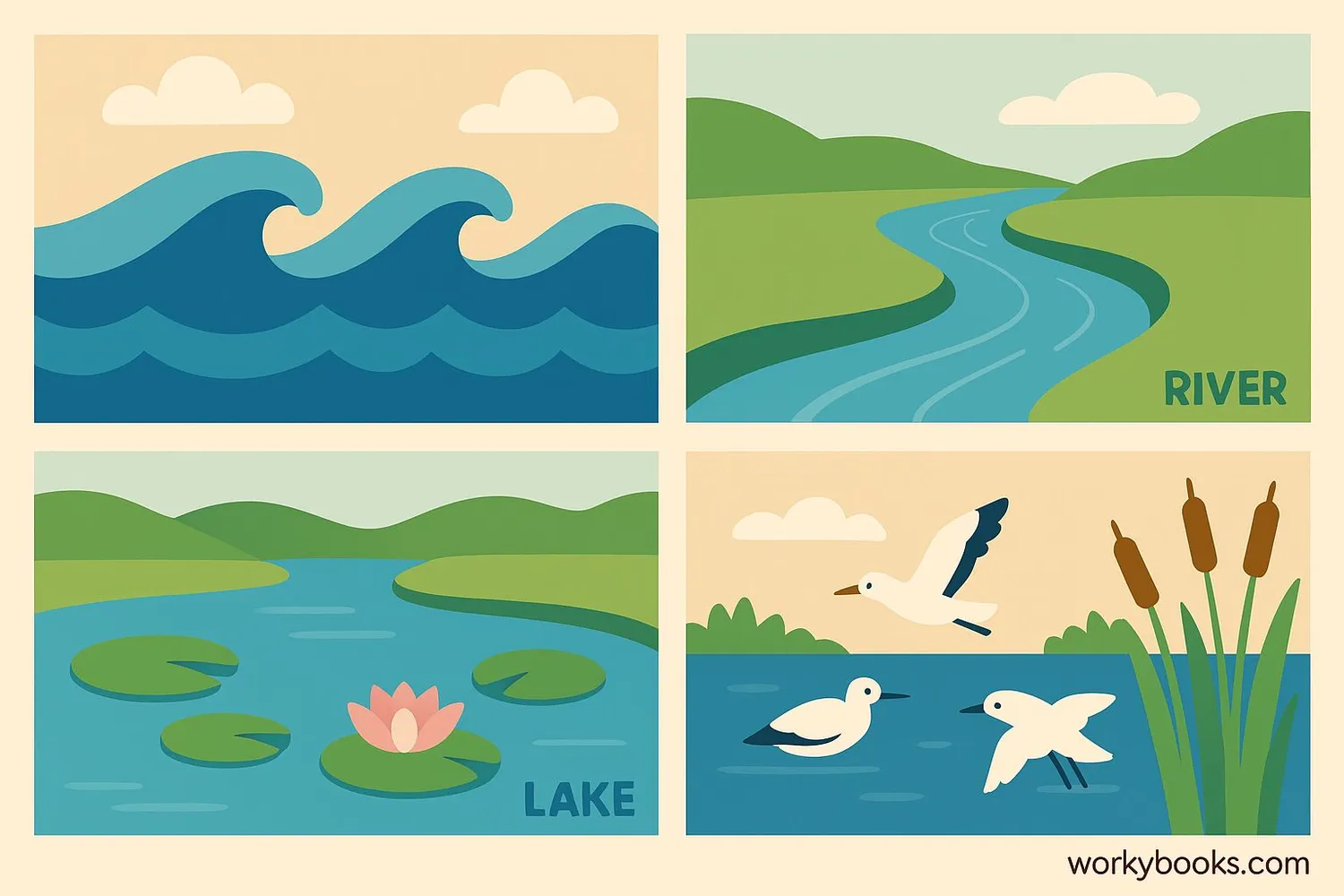

Aquatic biomes are water-based ecosystems that cover most of our planet! They're home to amazing plants and animals specially adapted to live in water.
Aquatic biomes can be divided into two main types: freshwater (with very little salt) and marine (saltwater). These water ecosystems are vital for life on Earth, providing habitats for countless species, regulating our climate, and supplying oxygen we breathe.
Water Fact!
Over 70% of Earth's surface is covered by water, making aquatic biomes the largest habitats on our planet!
Freshwater Biomes

Freshwater biomes have water with very little salt (less than 1%). These include:
Lakes and Ponds
Standing bodies of freshwater with still water
Rivers and Streams
Flowing water that moves in one direction
Wetlands
Areas where land is covered by water for part of the year
Freshwater biomes are home to special plants like submerged aquatic plants that grow completely underwater, and animals like fish, frogs, turtles, and insects. Wetlands are especially important because they filter water and provide homes for many species.
Freshwater Fact!
Although freshwater covers only about 2.5% of Earth's water, it's home to 10% of all known animal species!
Marine Biomes
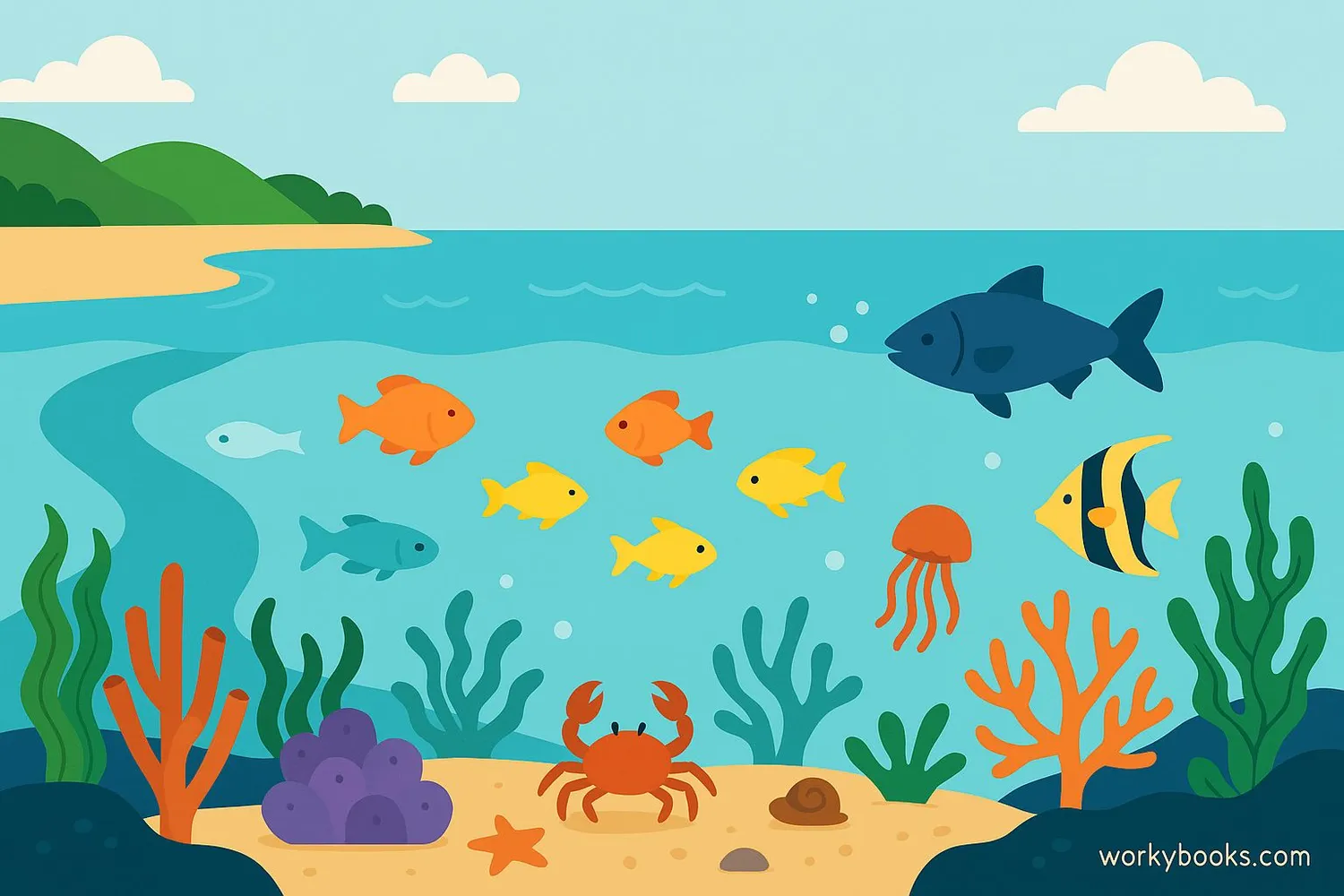

Marine biomes are saltwater ecosystems that cover most of Earth's surface. They include:
Oceans
Vast bodies of saltwater divided into different zones
Coral Reefs
Diverse underwater ecosystems built by corals
Estuaries
Where rivers meet the ocean, mixing fresh and salt water
Marine biomes are incredibly diverse! Oceans contain about 97% of Earth's water and are home to creatures from tiny plankton to giant whales. Coral reefs are often called the "rainforests of the sea" because of their amazing biodiversity.
Zones in Aquatic Biomes
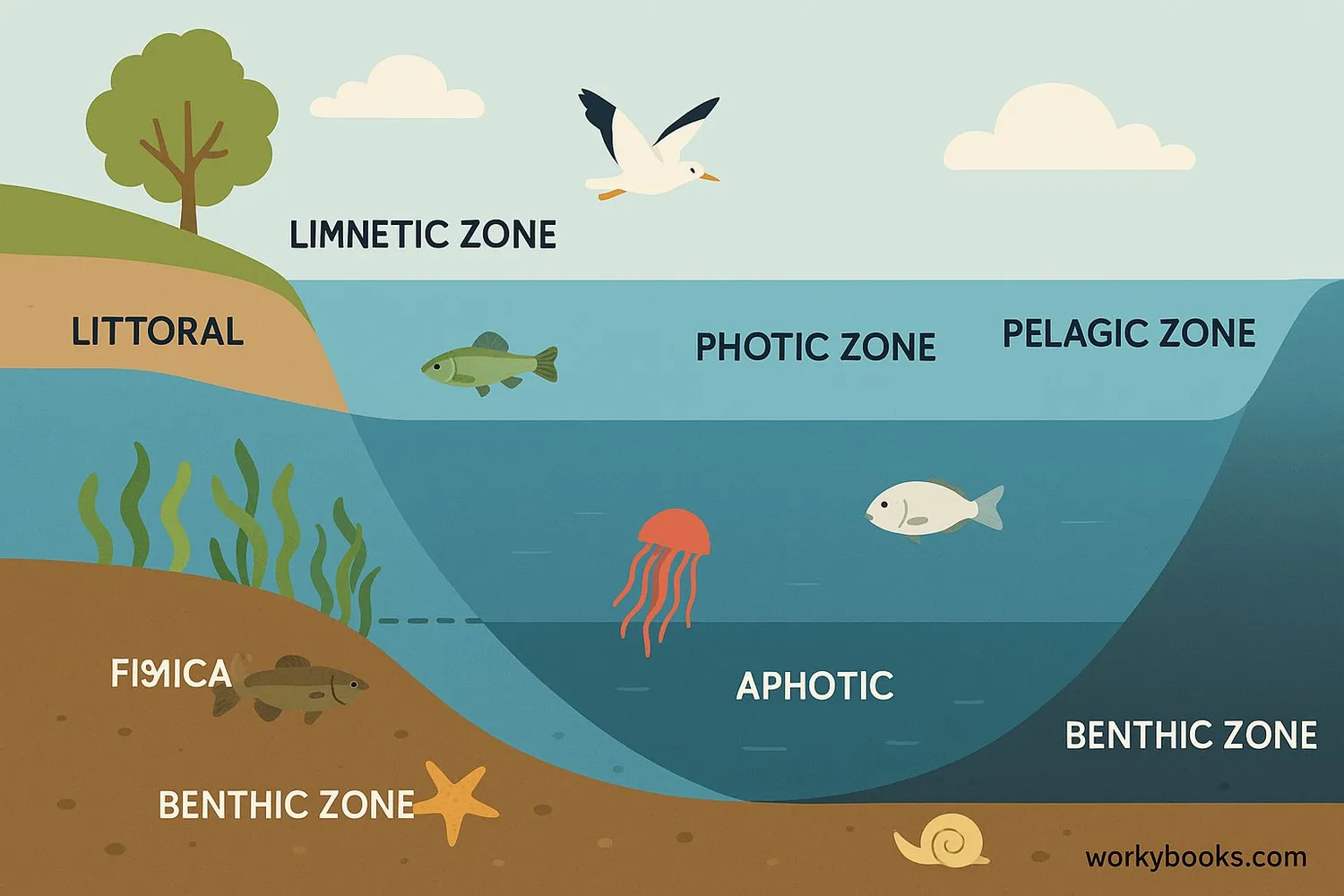
Aquatic biomes are divided into different zones based on depth, light, and location:
Photic Zone
Sunlight reaches here (top layer)
Aphotic Zone
No sunlight reaches here (deep water)
Pelagic Zone
Open water away from shore
Benthic Zone
Bottom of the water body
Littoral Zone
Shore area where light reaches bottom
Limnetic Zone
Open water in lakes where light penetrates
Each zone has special conditions that support different types of life. For example, the photic zone has plants that need sunlight for photosynthesis, while the aphotic zone has creatures that make their own light (bioluminescence) or feed on material sinking from above.
Aquatic Biomes Quiz
Test your knowledge about aquatic biomes with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about aquatic biomes:
Fun Aquatic Biomes Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about aquatic biomes!
Ocean Depths
We've explored less than 5% of Earth's oceans! The deepest part, the Mariana Trench, is deeper than Mount Everest is tall.
Coral Reef Cities
Coral reefs cover less than 1% of the ocean floor but are home to 25% of all marine species. That's why they're called the "rainforests of the sea"!
Mighty Rivers
The Amazon River releases so much freshwater into the Atlantic Ocean that you can drink from the ocean 100 miles from shore!
Ancient Lakes
Lake Baikal in Russia is the world's oldest and deepest freshwater lake. It's 25 million years old and contains 20% of Earth's unfrozen freshwater!





