What are Eukaryotic Cells? — Reading Comprehension
Premium Resource
Grades
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Standards
- MS-LS1-1
- MS-LS1-2
PRINT+DIGITAL RESOURCE
This learning resource is available in interactive and printable formats. The interactive worksheet can be played online and assigned to students. The Printable PDF version can be downloaded and printed for completion by hand.
About This Reader
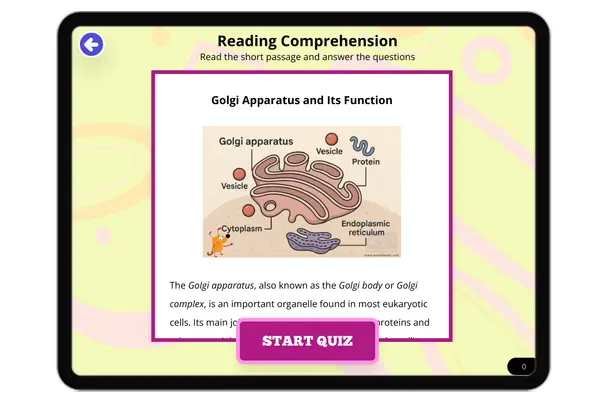
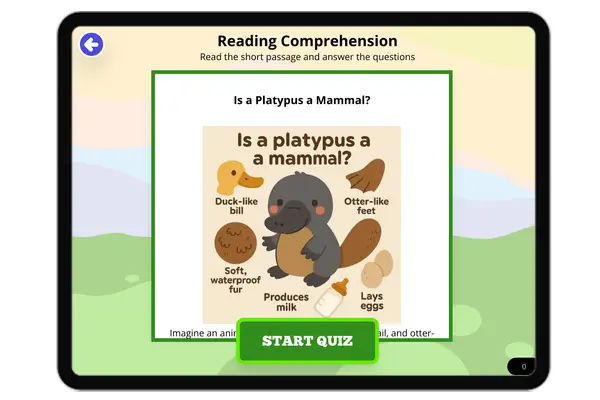
This NGSS-aligned reading passage introduces middle school students to eukaryotic cells, which are complex cells found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Supporting MS-LS1-1, the passage explains the role of the nucleus, DNA, and organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts. It emphasizes how eukaryotic cells allow for specialization in multicellular organisms. With accessible language and scientific vocabulary, this passage helps students build a deeper understanding of life science and cell structure while supporting Next Generation Science Standards in biology.
Perfect For:
👩🏫 Teachers
- • Reading comprehension practice
- • Auto-graded assessments
- • Literacy skill development
👨👩👧👦 Parents
- • Reading practice at home
- • Comprehension improvement
- • Educational reading time
🏠 Homeschoolers
- • Reading curriculum support
- • Independent reading practice
- • Progress monitoring
Reading Features:
📖
Reading Passage
Engaging fiction or nonfiction text
❓
Comprehension Quiz
Auto-graded questions
📊
Instant Feedback
Immediate results and scoring
📄
Printable Version
Download for offline reading