Reading Results
The Freezing Point of Water
This science reading passage, titled 'The Freezing Point of Water', introduces students to a key physical science concep...
MS-PS1-1RI.6.3RI.7.1
The Melting Point of Steel
This engaging science passage, 'The Melting Point of Steel,' explains a key physical property of steel—its melting point...
5-PS1MS-PS1-4RI.6.3RI.7.1
The Melting Point of Aluminum
This science reading passage, 'The Melting Point of Aluminum,' introduces middle school students to the physical propert...
5-PS1MS-PS1-4RI.6.3RI.7.1
The Melting Point of Copper
This reading passage, 'The Melting Point of Copper,' introduces middle school students to an important physical property...
5-PS1MS-PS1-4RI.6.3RI.7.1
The Boiling Point of Water
This passage, 'The Boiling Point of Water,' introduces students to the physical property of boiling point through one of...
5-PS1MS-PS1-4RI.6.3RI.7.1
The Mass of a Proton
This reading passage, 'The Mass of a Proton,' introduces middle school students to one of the smallest yet most importan...
MS-PS1HS-PS1RI.6.3RI.7.1
Do Protons and Electrons Have the Same Mass?
This reading passage, 'Do Protons and Electrons Have the Same Mass?', helps middle school students explore the massive d...
MS-PS1HS-PS1RI.6.3RI.7.1
What Charge Does a Neutron Have?
This middle school science passage, 'What Charge Does a Neutron Have?', teaches students about one of the key subatomic ...
MS-PS1HS-PS1RI.6.3RI.7.1
How Many Neutrons Does Hydrogen Have?
This reading passage, 'How Many Neutrons Does Hydrogen Have?', introduces middle school students to atomic structure usi...
MS-PS1HS-PS1RI.6.3RI.7.1
What Is the Charge of a Proton?
This reading passage, 'What Is the Charge of a Proton?', introduces middle school students to the concept of electric ch...
MS-PS1HS-PS1RI.6.3RI.7.1
What Is Thermal Contraction?
This middle school science passage introduces the concept of thermal contraction, aligned with NGSS standard MS-PS1-4. I...
MS-PS3-44-PS3-34-PS3-2
Sublimation: The Solid-to-Gas Magic
This engaging NGSS-aligned reading passage explores the science of sublimation, a unique phase change where a solid turn...
MS-PS3-44-PS3-34-PS3-2
Is Sublimation Endothermic or Exothermic?
This NGSS-aligned science passage for middle school explains the thermodynamic nature of sublimation, showing how a soli...
MS-PS1-4HS-PS1
How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have?
This NGSS-aligned science reading passage teaches middle school students about the number of valence electrons in oxygen...
MS-PS1-2MS-PS1-4
How Many Valence Electrons Does Chlorine Have?
This NGSS-aligned science reading passage explains how many valence electrons chlorine has and why that makes it such a ...
MS-PS1-2MS-PS1-4
The Density of Water
"This NGSS-aligned science passage explains the density of water in a way that is clear and engaging for middle school s...
MS-PS1-2
What Is Vapor Pressure?
This NGSS-aligned science passage explains the concept of vapor pressure in an age-appropriate, engaging way for middle ...
MS-PS1-4MS-LS1-2
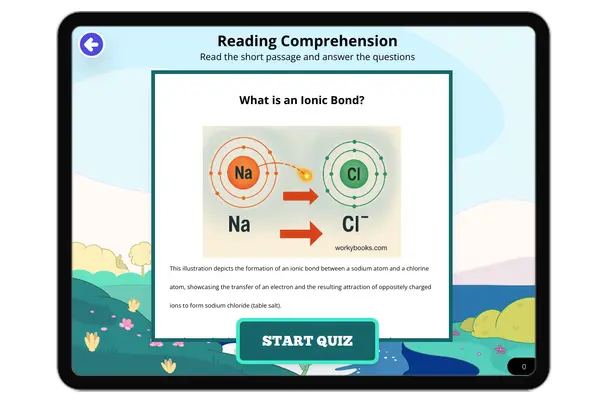
What is an Ionic Bond?
This science reading passage provides a clear and engaging explanation of ionic bonds for a middle school audience. It d...
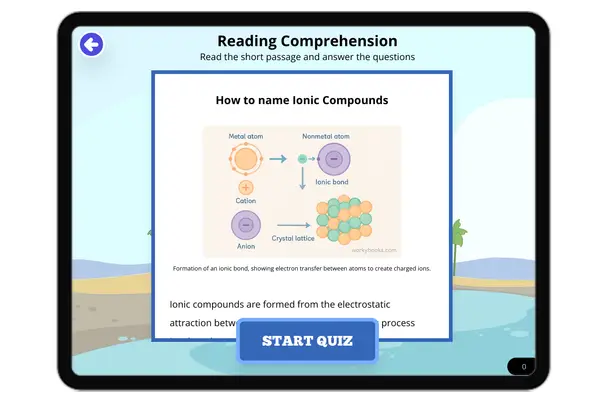
How to name ionic compounds
"This science passage, aligned with NGSS standards, provides a comprehensive explanation of how to name ionic compounds....
What are Valence Electrons
This science reading passage for middle school students delves into the concept of valence electrons, the outermost elec...
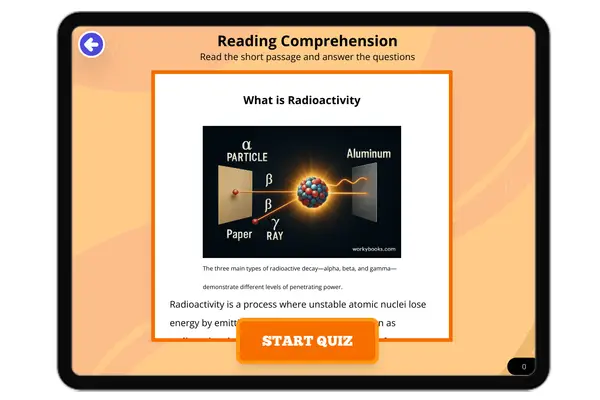
What is Radioactivity
This 300-350 word science reading passage provides a comprehensive overview of radioactivity for middle school students ...
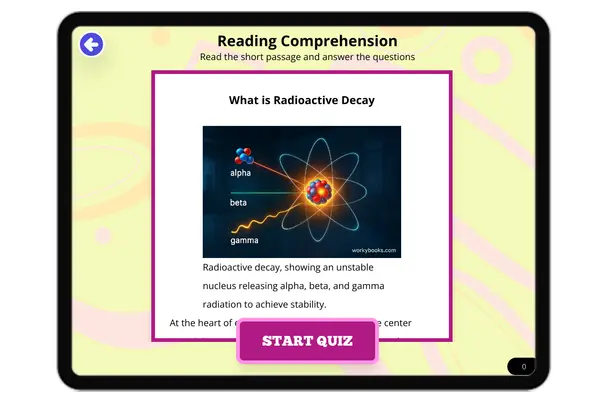
What is Radioactive Decay
"This comprehensive middle school science passage defines radioactive decay as the process by which unstable atomic nucl...
Acetic Acid Lewis Structure
"This learning module provides a comprehensive overview of the Lewis structure of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) for middle schoo...
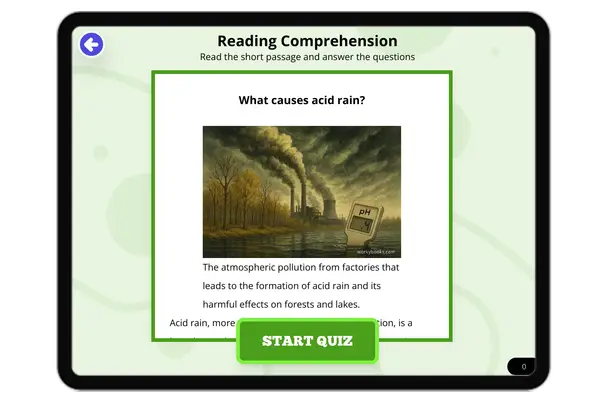
What causes Acid rain?
"This comprehensive reading passage for middle school students delves into the causes and effects of acid rain. Aligned ...
What is Freezing Point Depression
This passage, 'Freezing Point Depression,' introduces students to the physical science concept of how adding substances ...
5-PS1MS-PS1-4RI.6.3RI.7.1
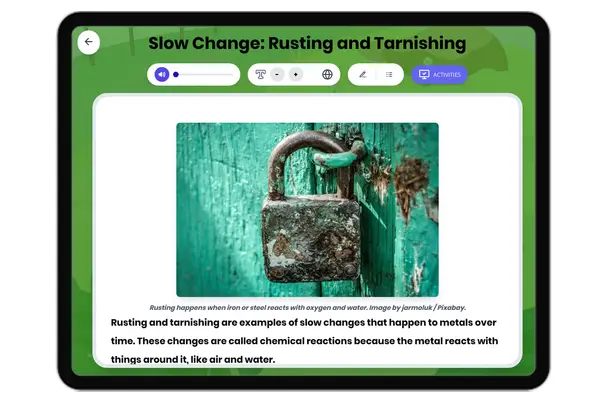
Slow Change: Rusting and Tarnishing
This NGSS-aligned reading passage introduces Grade 4-5 students to the science of slow changes in metals, focusing on ru...
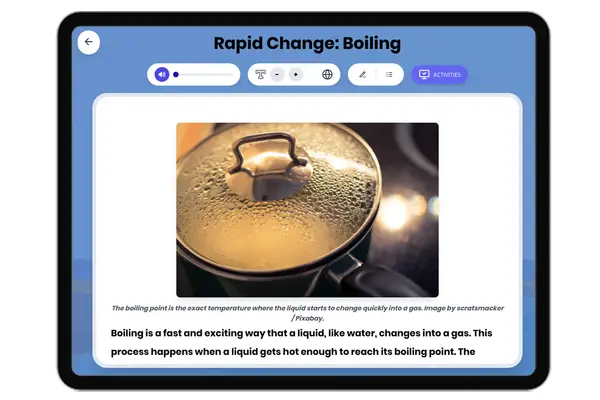
Rapid Change: Boiling
This engaging Grade 4-5 science passage explores 'Rapid Change: Boiling', aligning with NGSS standards for understanding...
Liquid to Solid: Freezing
This science passage, aligned to NGSS standards for Grade 4-5, introduces students to the process of freezing. Readers w...
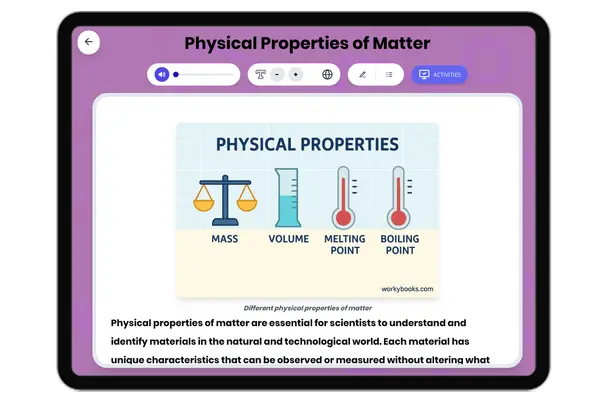
Physical Properties of Matter
This comprehensive reading passage introduces grades 6-8 students to the concept of physical properties of matter, perfe...
MS-PS1-1
Chemical Properties of Matter
This engaging middle school science passage explores the chemical properties of matter, focusing on how these properties...
MS-PS1-2
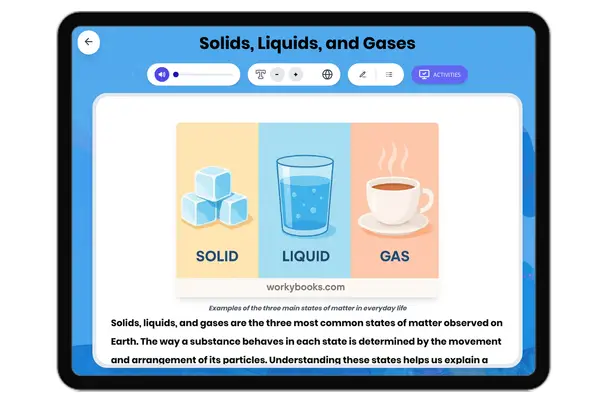
Solids, Liquids, and Gases
This comprehensive middle school science passage explains the scientific concepts behind the three common states of matt...
MS-PS1-4
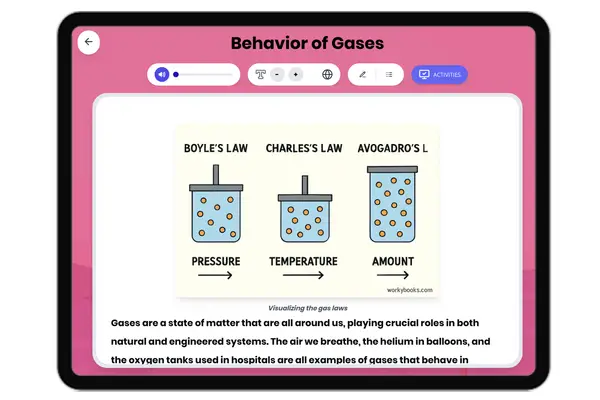
Behavior of Gases
This comprehensive reading passage explores the behavior of gases for middle school students, aligned with NGSS standard...
MS-PS1-4
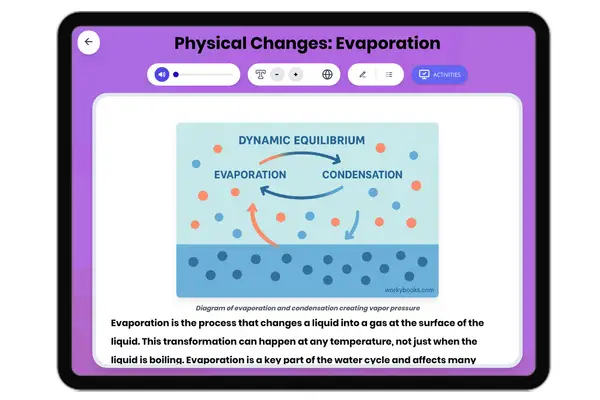
Physical Changes: Evaporation
This middle school science passage examines the process of evaporation, a fundamental physical change where a liquid tur...
MS-PS1-4
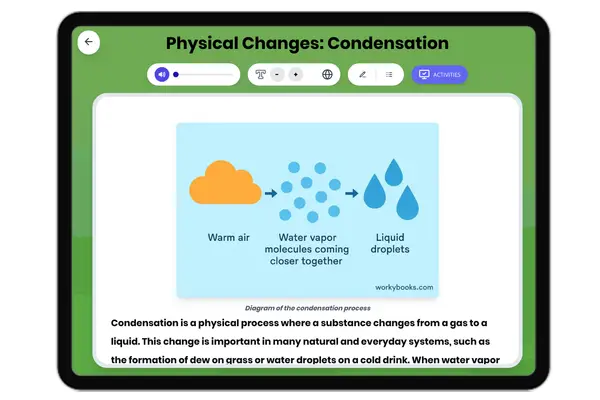
Physical Changes: Condensation
This middle school science passage explores the process of condensation, the physical change where a gas becomes a liqui...
MS-PS1-4
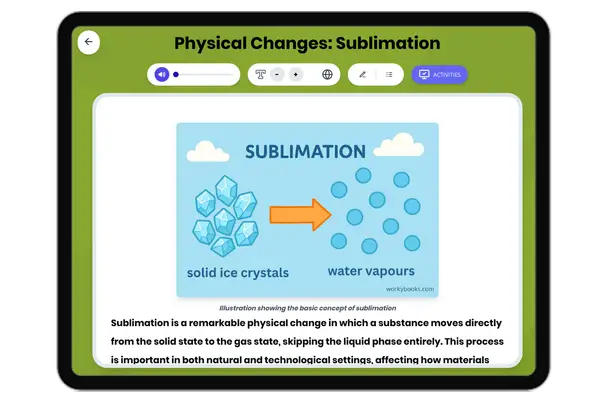
Physical Changes: Sublimation
This educational passage for grades 6-8 explores the science of sublimation—a physical change where a solid transforms d...
MS-PS1-4
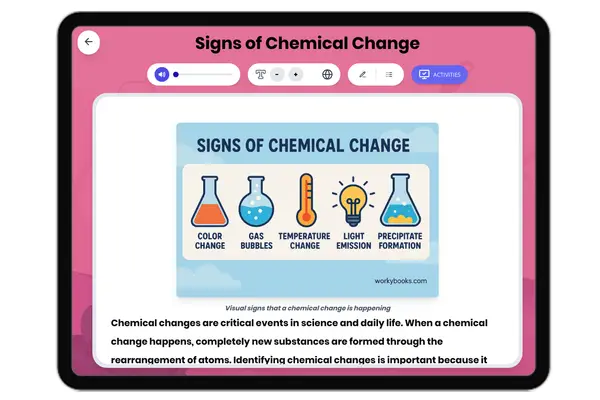
Signs of Chemical Change
This comprehensive passage for grades 6-8 explores the key signs that indicate a chemical change, such as color change, ...
MS-PS1-2
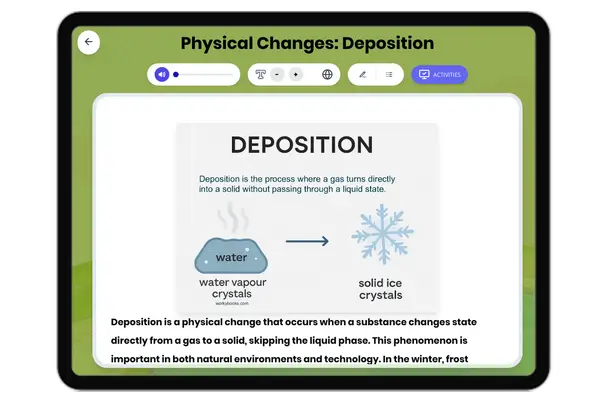
Physical Changes: Deposition
This middle school science passage explores the concept of deposition, a type of physical change where matter transition...
MS-PS1-4
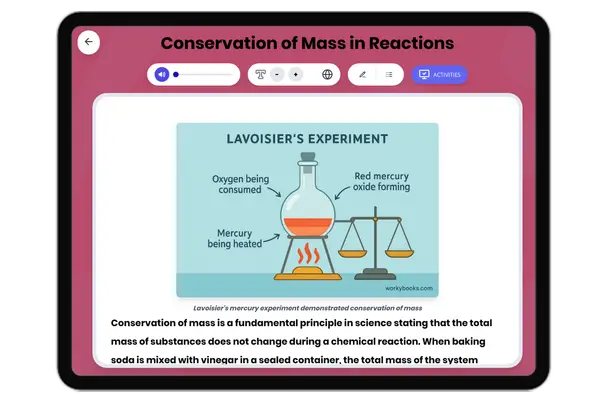
Conservation of Mass in Reactions
This science reading passage for grades 6-8 dives into the concept of conservation of mass during chemical reactions, em...
MS-PS1-5
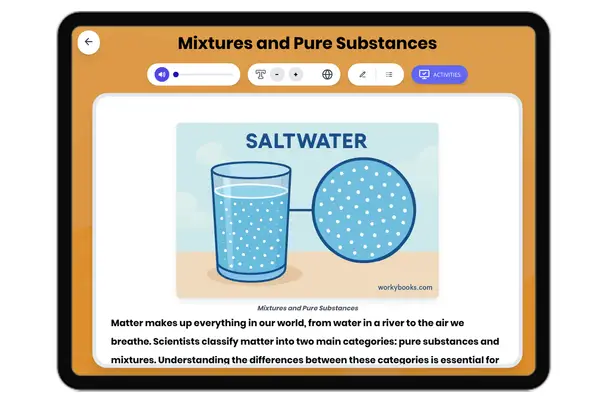
Mixtures and Pure Substances
This middle school science passage provides an in-depth exploration of mixtures and pure substances, directly aligned to...
MS-PS1-1
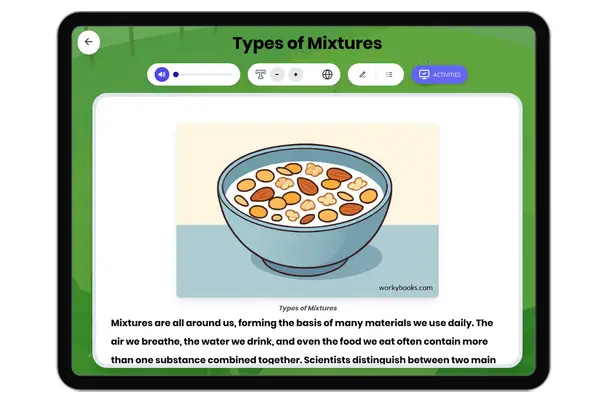
Types of Mixtures
This comprehensive science passage for grades 6-8 introduces students to the concept of mixtures, focusing on distinguis...
MS-PS1-1
Solutions, Suspensions, and Colloids
This comprehensive science passage explores the differences between solutions, suspensions, and colloids, focusing on ho...
MS-PS1-1
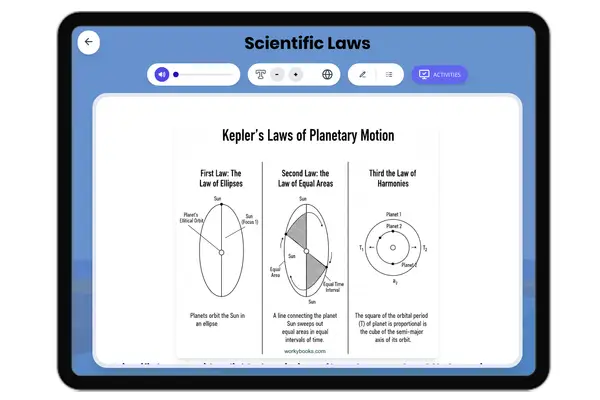
Scientific Laws
This comprehensive middle school science passage introduces students to scientific laws, focusing on how they describe c...
MS-PS2-4MS-PS1-5MS-ETS1-4
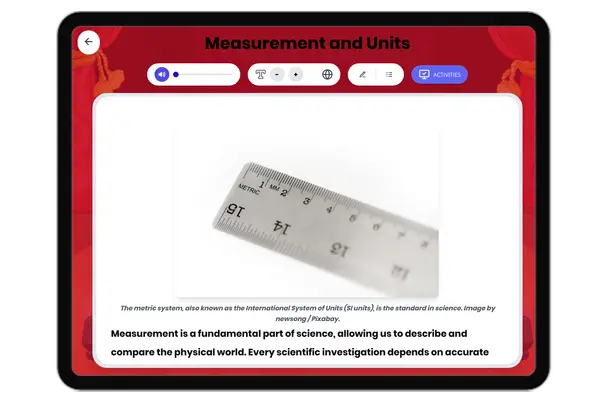
Measurement and Units
This comprehensive passage introduces middle school students to the foundational concepts of measurement in science, foc...
MS-PS1-2MS-ETS1-4
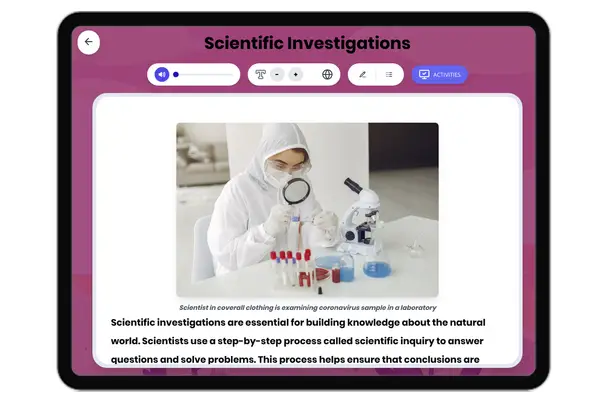
Scientific Investigations
This passage, aligned with NGSS standards for grades 6-8, introduces students to the process of scientific investigation...
MS-ETS1-1MS-ETS1-2MS-ETS1-3MS-ETS1-4
The Nature of Science
This passage explores the nature of science for middle school students, aligning with NGSS standards MS-ETS1-4, MS-PS1-1...
MS-ETS1-4MS-PS1-1MS-LS1-1
Scientific Theories
This reading passage for grades 6-8 introduces students to the concept of scientific theories, emphasizing that these ar...
MS-PS1-1MS-PS1-4MS-PS3-4SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PRACTICES
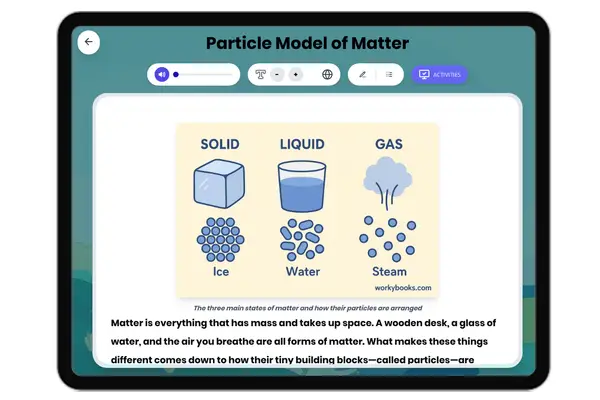
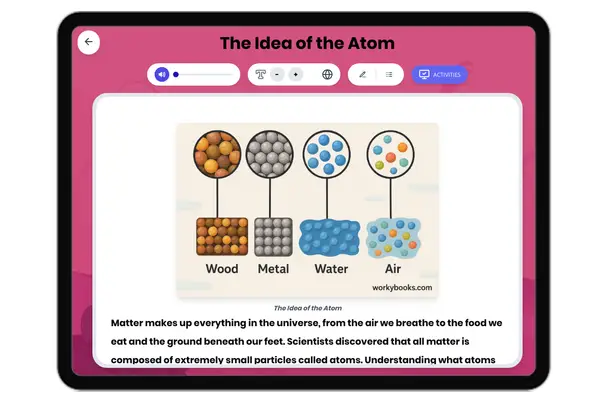
Particle Model of Matter
This comprehensive science reading passage for grades 6-8 explores the particle model of matter, aligning with NGSS stan...
MS-PS1-1MS-PS1-4
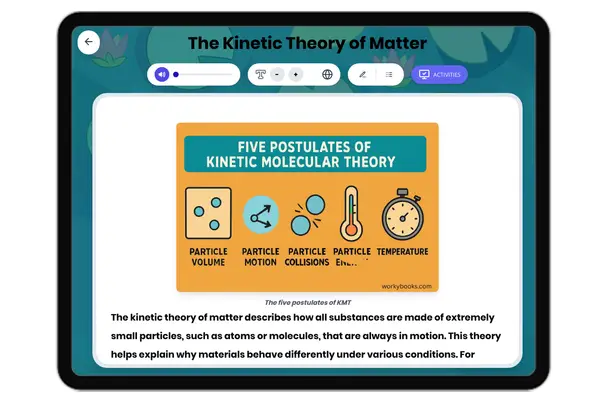
Kinetic Theory of Matter
This middle school science reading passage introduces students to the kinetic theory of matter, aligning with NGSS MS-PS...
MS-PS1-4
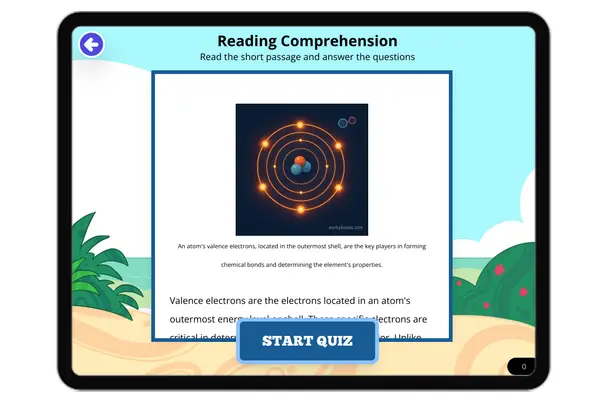
Valence Electrons
This middle school science passage introduces students to the concept of valence electrons, the outermost electrons that...
MS-PS1-1